
The Molecular Mechanisms of Cancer and Stemness group is fully dedicated to the identification of elements and pathways that regulate Stem Cell and Cancer Stem Cell homeostasis, with the final goal of discovering biomarkers and therapeutic targets for regenerative medicine and cancer.
The group has historically focused on studying the Notch and NF-κB pathways, which are principal actors of these processes. However, our research now aims to integrate these pathways in the context of other important signals for stem cell and cell transformation such as BRAF or β-catenin.
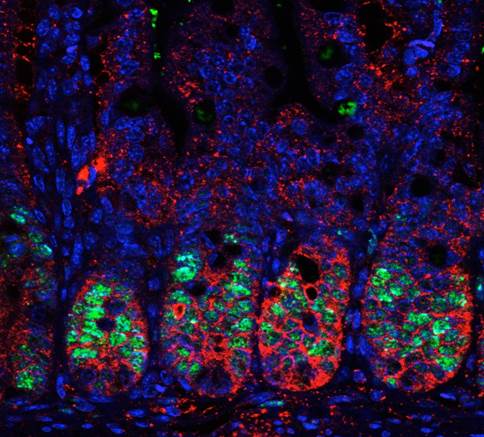
Thus our current interest lays on two different subjects: 1) the identification of the cellular compartments that are regulated by PS-IκBα and the mechanisms supporting this selectivity, and 2) the investigation of p45-IKKα function in stem cells, tissue homeostasis and oncogenic transformation, mainly through the identification and characterization of its phosphorylation targets and the genomic regions that are substrates for p45-IKKα.
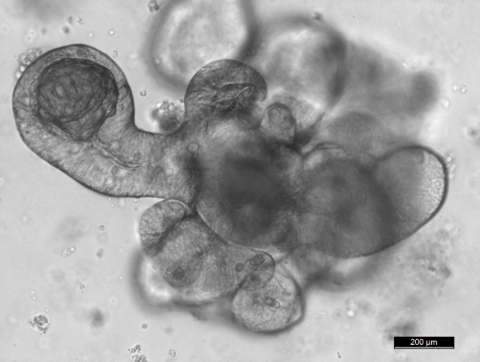
To achieve our objectives, we are setting up a variety of cutting-edge in vivo and in vitro models including 3D cultures for intestinal stem cells (miniguts), tissue-specific and/or inducible knock out and transgenic mice lines, and reporter animals for stem cell and tumor cell lineage tracing experiments.
Coordinator:
Lluís Espinosa(ELIMINAR)
Tel:
933160589
Dr.Aiguader, 88, 2ª Planta
08003 Barcelona
© Institut Hospital del Mar
d'Investigacions MèdiquesLegal Notice and Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy | Site Index | Accessibility | Find Us | Contact